Fanless PC
Understanding the Effect of Heat on Your Computer: Should You Be Concerned?
Jarltech's fanless embedded computers are advanced systems designed for edge computing, making them highly suitable for remote monitoring and control tasks.
Our selection features an array of I/O products that are modular and readily available, allowing customers to quickly implement a wide range of applications and fully realize the resulting benefits.
Which components generate heat?
The CPU is the computer's central component that creates heat when executing algorithms, while the GPU, responsible for 3D imaging on the screen, also contributes to heat production.
Intensive gaming sessions can cause temperatures to rise due to the heavy reliance on GPUs for complex computations. Often, the GPU produces more heat than the CPU.
Hard drives can contribute to increased heat generation, especially during the transfer of large files.
What is the Influence of Heat on Your Hard Drive?
While hard disk drives (HDDs) consume less power than the CPU or GPU, they are extremely sensitive to temperature changes and excess heat can result in irreversible damage to your hard drive.
In physics, it's a simple concept: cold causes contraction, while heat causes expansion. Heat transfer resulting in thermal expansion can distort internal components, causing problems in reading discs. Although extreme, it may require replacing the HDD.
Elevated temperatures can significantly reduce the lifespan of your hard drive. National Instruments reports that increasing the temperature by just 5°C above the ambient room temperature could potentially decrease the expected lifespan of a drive by up to two years.
While there is ongoing debate regarding the correlation between disk drive failure rates and increased temperatures, prominent Google engineers have concluded that other factors likely play a more significant role in failure rates within moderate temperature ranges.
The effect is greater on older hard drives, particularly those exceeding three years. Usually, it is possible to recover data, but dealing with a damaged hard drive can be more complicated.
What Keeps a Fanless PC Cool?
Compared to a traditional computer with fans, including compact models, a fanless PC may not have a noticeably distinct appearance.
Nonetheless, various inconspicuous processes prevent these simple hardware components from overheating.
Fanless computers often cool down through the principle of conduction. This occurs when a hot object dissipates heat into its surroundings through direct physical contact.
Although heat conduction is a natural process, the design can greatly influence the amount of heat dissipation.
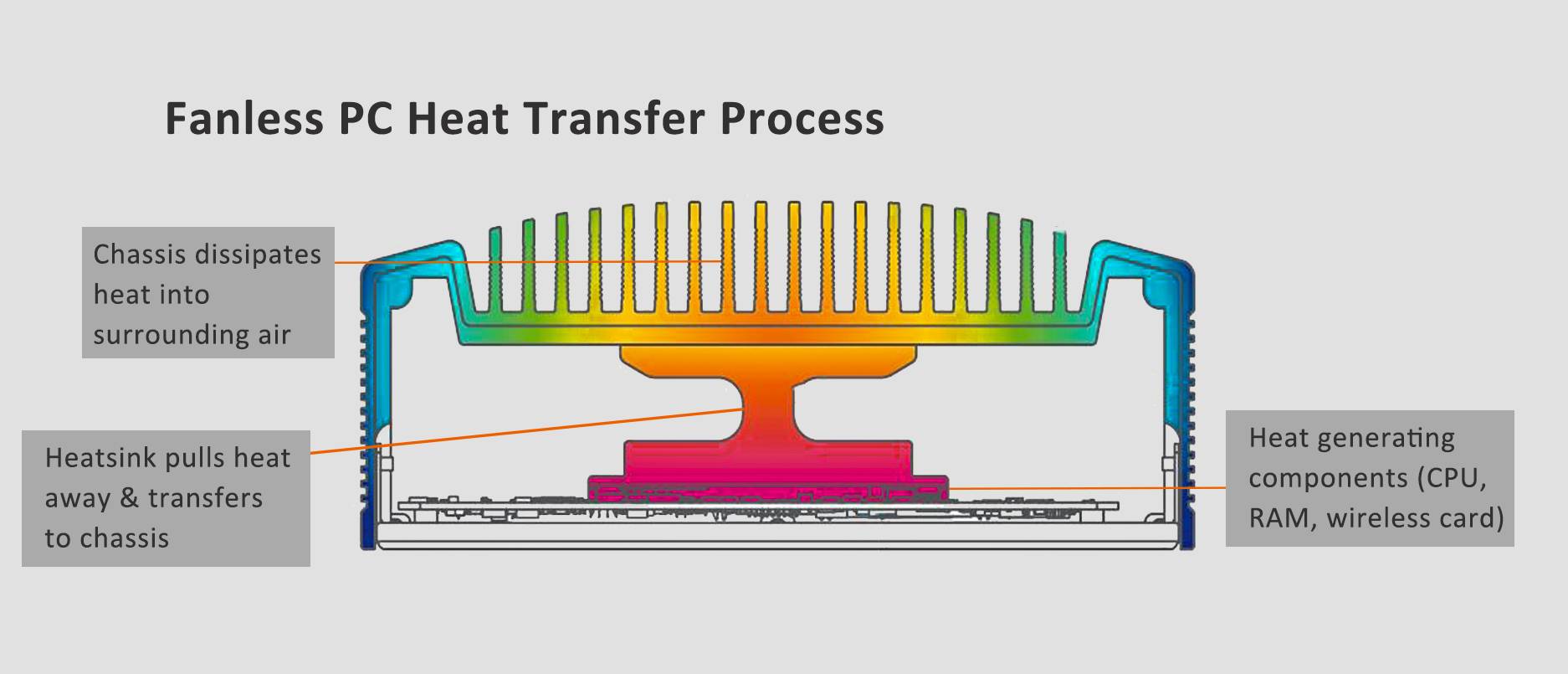
The main concept is to have heat-generating components, like a computer's CPU, in direct contact with a heat sink. The heat sink facilitates the dissipation of the heat generated by these components into the surrounding air.
When designing a heat sink, consider the materials you will use and how the components will interact. It's important to ensure that all elements work together effectively.
What Types of Materials Are Employed in Heat Sinks?
It makes sense to utilize a heat conductor when constructing a heat sink. Just like an electrical conductor enables the flow of electrical current, a heat conductor is a material that readily allows the transfer of heat.
When a hot object like a CPU is touching one end of a heat conductor while something relatively cold, such as the air outside of the computer, is in contact with the other side, heat will transfer between the two materials.
Heat dissipates quickly from the heat source through the conductor. Copper and aluminum are the preferred materials for heat sink conductors in the industry.
The majority of heat sink assemblies in logic supply consist of two main parts: an aluminum block attached to the top of the CPU and the case lid.
Heat transfers from the CPU to the aluminum block and then to the lid. The heat ultimately dissipates into the surrounding atmosphere.
Efficiently cooling the system necessitates efficient heat-conducting interfaces among all of the components.
Creating a High-Performance Heat-Conducting Interface
Establishing an efficient heat transfer interface requires different strategies for the interior and exterior of the PC. As air is a poor conductor of heat, it is essential to minimize its presence between the CPU and the heat sink within the PC.
Developing an efficient heat transfer interface for a PC requires distinct strategies for both the interior and exterior. Because air is a poor heat conductor, it's crucial to minimize any air presence between the CPU and heat sink within the PC.
Thermal paste conducts heat more efficiently than air by filling any gaps that would otherwise be filled with air. Externally, the PC releases heat directly into the surrounding air requiring a unique approach. A commonly utilized design incorporates a lid featuring specially engineered ridges.
These ridges increase the amount of surface area in contact with the air, creating additional avenues for heat to dissipate.
By adhering to these principles, you can avoid common mistakes when assembling or using a Fanless PC. For example, although thermal paste conducts better than air, it is significantly less effective than metals such as copper or aluminum.
Use only enough thermal paste to fill the necessary gaps. An excess amount can create a thermal barrier and cause overheating. Also, avoid placing objects on top of a Fanless computer as it can cause complications.
Even a single sheet of paper can create a pocket of hot air on the lid of the computer, impeding the cooling process.
Consider the airflow around the PC. When in enclosed areas or at high altitudes where airflow is limited or thin, the ability to dissipate heat from the PC decreases.
Jarltech Fanless Embedded Computers are specialized systems made specifically for edge computing, which makes them highly suitable for tasks such as remote monitoring and control.
Jarltech offers a range of modular and easily accessible I/O products that assist clients in promptly implementing diverse applications to maximize their benefits.
Fanless PC | High-Quality Self-Service Kiosk Solutions | Jarltech
Located in Taiwan since 1987, Jarltech International Inc. has been a developer and manufacturer of POS and Kiosk systems for restaurants, retail stores and supermarkets. Their main software and hardware products include, Fanless PC, small business POS systems, self-service kiosks, smart card readers, Bluetooth thermal printers, embedded motherboards and all-in-one panel PCs, focusing on providing interactive kiosk solutions.
Leverage Jarltech’s 30+ years of expertise in developing innovative POS and Kiosk systems tailored for diverse business needs in restaurants, retail stores, and supermarkets. Our specialized solutions, encompassing IPC, Touch Monitor, Thermal Printer, and Smart Card Reader, are designed to elevate your business operations, ensuring seamless transactions and enhanced customer experiences.
Jarltech has been offering customers global B2B solutions with Jarltech’s POS and Kiosk Systems since 1987, both with advanced technology and 35 years of experience, Jarltech ensures each customer's demands are met.